Following years of development and testing, UV Pure launched the third generation of our popular Hallett UV water disinfection system. As we ramp up production to meet global demand, we want to share how the new Hallett makes safe water more accessible than ever.
Versatile UV water disinfection for diverse needs
The new Hallett offers the same reliable water disinfection for a wide range of applications. Our new product lineup includes models with varying capacities divided into three categories: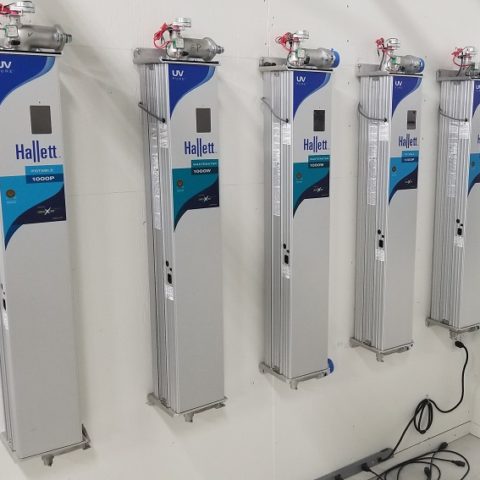
- Hallett P models for potable water applications, such as commercial and residential use. The 500PN and 750PN are available with NSF 55A certification. The 1000P is available with EPA validation.
- Hallett W models for wastewater applications, including industrial use. The 1000W is available with EPA validation.
- Hallett R for reuse applications, such as in agricultural and recreational settings. The 1000R is available with NWRI validation for water reuse.
Third-party validation is pending for the Hallett 500 & 750 R, W models.
Our new Hallett 1000 models have been validated for US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) performance standards for UV water disinfection to service markets that require EPA validation.
Larger, more powerful units
One of the exciting developments with the third-generation Hallett, is the introduction of high-capacity models. These models can handle flow rates up to 100gpm, up from the previous maximum of 30gpm. For applications requiring higher flows, like municipal water systems, multiple Hallett 1000’s can be connected to allow flows up to 1MGD.
For enhanced performance, these larger units feature amalgam lamps with higher output and an extended lamp life of up to 12,000 hours. Some larger models also come with quad UV sensors to support higher-accuracy measurements of UV dose and UV transmittance (UVT).
Smarter technology and improved design
Incorporating years of feedback from customers, technicians and our in-house experts has helped us make major technology and design enhancements in the new Hallett. Here are a few highlights:
- UV dose display to enable hourly, daily, or weekly dose recording
- A real-time clock to facilitate troubleshooting with time and date stamps for errors and warnings
- A wiper position switch to accurately sense wiper movements in low UVT applications and optimize the wiper parking position
- Data logging at 30-second intervals on a USB key
- A double door hinge design to allow easier lamp changes and servicing of system components
- Improved UV sensor housing to protect sensors during system handling and sensor calibration
Optimized performance and remote operation
Dependable performance is crucial to ensure that our Hallett systems can provide safe water in varying operating environments. That’s why the third-generation Hallett features forced-air cooling to prevent overheating and lamp heaters to enable use in extreme conditions.
Dependability also means that users can trust that their systems are running well, even when they’re not on site. Remote start/stop capabilities mean the new Hallett can remain on standby until a remote signal starts the UV system. The new models also provide more system information to remote operators, allowing them to prevent possible shutdowns ahead of any issues.
Delivering safe, clean water through innovation
Global demand for safe water continues to grow and innovations in water technology are rising to the challenge. As a pioneer in UV water disinfection, UV Pure continues to help customers meet their water needs across diverse industries, applications and markets.
If you would like to learn more about the new Hallett’s technical specifications and how it can meet your water requirements, please contact our business development team.



 UV disinfection systems intended for use at a public or commercial site (e.g. hospital, campground, hotel, etc.) generally require certification. In these settings, certification is essential for protecting public health, meeting compliance obligations and managing liability.
UV disinfection systems intended for use at a public or commercial site (e.g. hospital, campground, hotel, etc.) generally require certification. In these settings, certification is essential for protecting public health, meeting compliance obligations and managing liability.
 Each technology has a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. For example, chemical disinfection using chlorine is highly reliable and inexpensive, but it poses safety risks in the handling of chlorine and the creating toxic byproducts.
Each technology has a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. For example, chemical disinfection using chlorine is highly reliable and inexpensive, but it poses safety risks in the handling of chlorine and the creating toxic byproducts.